anti-c-Fos antibody
| 产品描述 | Rabbit Polyclonal antibody recognizes c-Fos |
|---|---|
| 反应物种 | Hu, Ms, Rat, Cow, Hrs, Pig |
| 预测物种 | Chk |
| 应用 | ICC/IF, IHC-Fr, WB |
| 宿主 | Rabbit |
| 克隆 | Polyclonal |
| 同位型 | IgG |
| 靶点名称 | c-Fos |
| 抗原物种 | Human |
| 抗原 | Full length recombinant Human protein expressed in and purified from E. coli. |
| 偶联标记 | Un-conjugated |
| 別名 | Proto-oncogene c-Fos; C-FOS; AP-1; Cellular oncogene fos; p55; G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 7 |
| 应用建议 |
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 应用说明 | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
| 形式 | Liquid |
|---|---|
| 纯化 | Affinity purification. |
| 缓冲液 | PBS and 50% Glycerol. |
| 稳定剂 | 50% Glycerol |
| 浓度 | 1 mg/ml |
| 存放说明 | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| 注意事项 | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
| 数据库连接 | |
|---|---|
| 基因名称 | FOS |
| 全名 | FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| 背景介绍 | The Fos gene family consists of 4 members: FOS, FOSB, FOSL1, and FOSL2. These genes encode leucine zipper proteins that can dimerize with proteins of the JUN family, thereby forming the transcription factor complex AP-1. As such, the FOS proteins have been implicated as regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and transformation. In some cases, expression of the FOS gene has also been associated with apoptotic cell death. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| 生物功能 | Nuclear phosphoprotein which forms a tight but non-covalently linked complex with the JUN/AP-1 transcription factor. In the heterodimer, FOS and JUN/AP-1 basic regions each seems to interact with symmetrical DNA half sites. On TGF-beta activation, forms a multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex at the AP1/SMAD-binding site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated signaling. Has a critical function in regulating the development of cells destined to form and maintain the skeleton. It is thought to have an important role in signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. In growing cells, activates phospholipid synthesis, possibly by activating CDS1 and PI4K2A. This activity requires Tyr-dephosphorylation and association with the endoplasmic reticulum. [UniProt] |
| 产品亮点 | Related products: Anti-Rabbit IgG secondary antibodies; Related news: Viral-like capsids, new trans-synaptic mRNA transport mechanism |
| 研究领域 | Cancer antibody; Gene Regulation antibody; Neuroscience antibody; AP-1 early response transcription factor study antibody |
| 预测分子量 | 41 kDa |
| 翻译后修饰 | Phosphorylated in the C-terminal upon stimulation by nerve growth factor (NGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Phosphorylated, in vitro, by MAPK and RSK1. Phosphorylation on both Ser-362 and Ser-374 by MAPK1/2 and RSK1/2 leads to protein stabilization with phosphorylation on Ser-374 being the major site for protein stabilization on NGF stimulation. Phosphorylation on Ser-362 and Ser-374 primes further phosphorylations on Thr-325 and Thr-331 through promoting docking of MAPK to the DEF domain. Phosphorylation on Thr-232, induced by HA-RAS, activates the transcriptional activity and antagonizes sumoylation. Phosphorylation on Ser-362 by RSK2 in osteoblasts contributes to osteoblast transformation (By similarity). Constitutively sumoylated with SUMO1, SUMO2 and SUMO3. Desumoylated by SENP2. Sumoylation requires heterodimerization with JUN and is enhanced by mitogen stimulation. Sumoylation inhibits the AP-1 transcriptional activity and is, itself, inhibited by Ras-activated phosphorylation on Thr-232. In quiescent cells, the small amount of FOS present is phosphorylated at Tyr-10 and Tyr-30 by SRC. This Tyr-phosphorylated form is cytosolic. In growing cells, dephosphorylated by PTPN2. Dephosphorylation leads to the association with endoplasmic reticulum membranes and activation of phospholipid synthesis. |
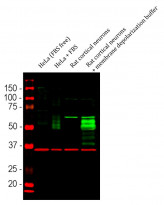
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody WB image
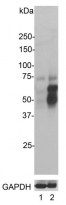
Western blot: 1) HeLa (FBS free), 2) HeLa treated with 20% FBS for 2 hours after being in FBS free media for 36 hours, 3) Rat cortical neurons and 4) Rat cortical neurons treated with membrane depolarization buffer for 5 hours. The blots were stained with ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody (green) at 1:5000 dilution and ARG52320 anti-GAPDH antibody [1D4] (red) at 1:5000 dilution.
Multiple bands at 50-65 kDa correspond to different isoforms of the c-FOS protein.
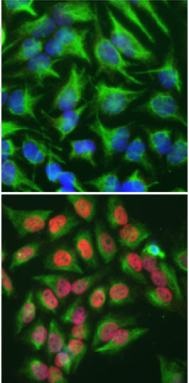
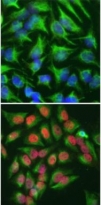
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody ICC/IF image
Immunocytochemistry: ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody staining (red) in HeLa cells which were treated with serum-starvation for 36 hours, followed by 2 hours, 20% FBS stimulation (bottom panel), or followed by PBS treatment (top panel). Red c-Fos staining only localizes in the nuclei of stimulated cells, but not in un-stimulated cells. Cells were co-stained with a chicken polyclonal antibody against vimentin (green). Blue shows DAPI staining of nuclear DNA.
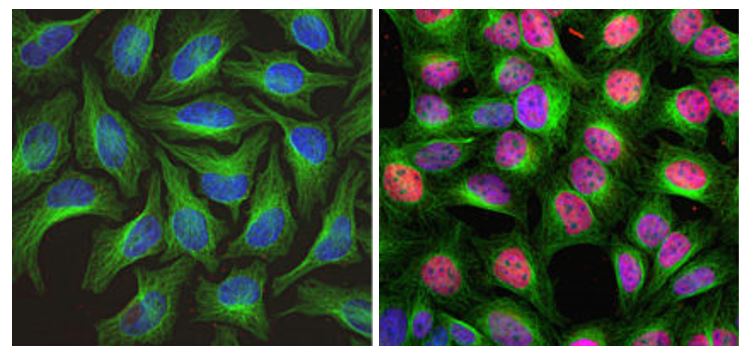
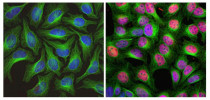
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody ICC/IF image
Immunofluorescence: HeLa cells stained with ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody (red) at 1:5000 dilution and Mouse mAb to tubulin (green) at 1:10000 dilution. DAPI (blue) for nuclear staining.
HeLa cells were kept in fetal bovine serum (FBS) - free media for 36 hours. Then the cells were treated with PBS (left), as a control, or stimulated with 20% FBS (right) for 30 min. c-FOS antibody labels only the nuclei of stimulated cells.
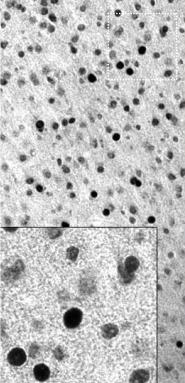
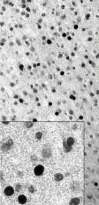
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody IHC image
Immunohistochemistry: Mouse brain section (45 µM; fixed by transcardial perfusion with 4% paraformaldehyde) stained with ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody using a standard HRP-DAB staining technique. Cells expressing c-Fos appear to be dark.
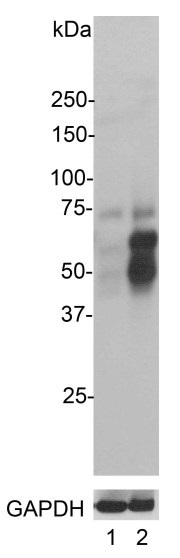
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody WB image
Western blot: Top panel: 1) HeLa cells were serum-starved for 36 hours, and 2) Serum-starved HeLa cells were stimulated with 20% FBS (fetal bovine serum) for 2 hours. ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody recognizes bands with apparent molecular weight of 50-65 kDa, representing multiple forms of the c-Fos protein. These bands appear in serum stimulated cells and are absent in serum-starved HeLa cells. Bottom panel: Blot was stripped and stained with a monoclonal antibody (Clone: 1D4) against GAPDH, used as loading control.
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody ICC/IF image
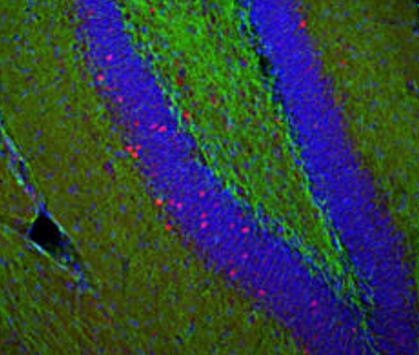
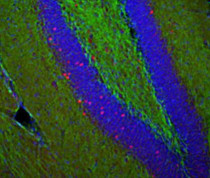
Immunofluorescence: Mouse hippocampus sections stained with ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody (red) at 1:20000 dilution and Mouse mAb to NF-L (green) at 1:5000 dilution. DAPI (blue) for nuclear staining. Following transcardial perfusion of Mouse with 4% paraformaldehyde, brain was post fixed for 24 hours, cut to 45 µM, and free-floating sections were stained with above antibodies.
The c-FOS antibody stains only nuclei of spontaneously active neurons. NF-L is expressed in axons of neuronal cells.
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody ICC/IF image
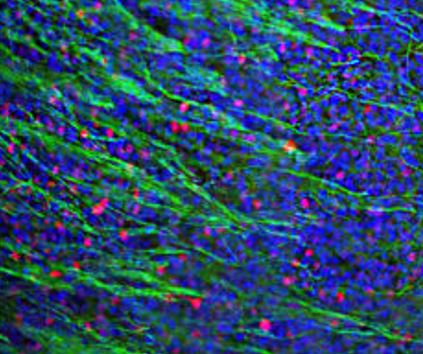
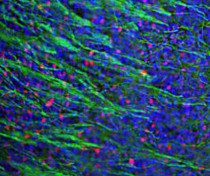
Immunofluorescence: Mouse olfactory bulb sections stained with ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody (red) at 1:20000 dilution and Mouse mAb to NF-L (green) at 1:5000 dilution. DAPI (blue) for nuclear staining. Following transcardial perfusion of Mouse with 4% paraformaldehyde, brain was post fixed for 24 hours, cut to 45 µM, and free-floating sections were stained with above antibodies.
The c-FOS antibody stains only nuclei of spontaneously active neurons. NF-L is expressed in axons of neuronal cells.
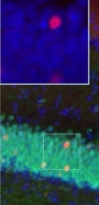
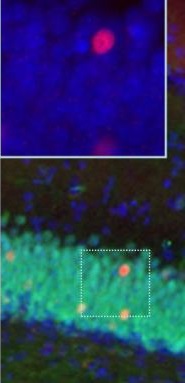
ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody IHC-Fr image
Immunohistochemistry: Frozen sections of Mouse brain across hippocampus stained with ARG10733 anti-c-Fos antibody (red) and co-stained with anti-Fox3 / NeuN antibody (green) using immuno-fluorescent microscopy. Neurons positive for c-Fos and Fox3 / NeuN appear to be yellow. Inset shows an enlarged image. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
 New Products
New Products