Human MBL2 ELISA Kit
Mannan binding lectin (MBL) belongs to the collectin family of innate immune defense proteins, which binds to an array of carbohydrate patterns on pathogen surfaces. Collectin family members share common structural features: a cysteine rich amino-terminal domain, a collagen-like region, an alpha -helical coiled-coil neck domain and a carboxy terminal C-type (Ca++-dependent) lectin or carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD). MBL homotrimerizes to form a structural unit joined by N-terminal disulfide bridges. These homotrimers further associates into oligomeric structures of up to 6 units. Whereas two forms of MBL proteins (MBL-1, also known as S-MBP or MBL-A and MBL-2, also known as L-MBP or MBL-C) exist in rodents and other animals, only one functional MBL protein is present in humans. Mouse MBL-2 shares about 52% and 60% amino acid sequence identity with mouse MBL-1 and human MBL, respectively.
In mouse, MBL-1 and MBL-2 are the only collectins that can activate complement via the lectin complement pathway. Serum oligomeric MBL associates with MBL-associated serine protease (MASP) proenzymes. The MBL-MASP proenzyme complex preferentially interact with sugar patterns containing mannose, glucose, L‑fucose, or N-acetyl-glucosamine present at a terminal nonreducing postion on the cell surface of various pathogens and certain tumor cells. This interaction induces pro-enzyme activation and the triggering of the complement cascade, resulting in opsonization and pathogen removal via humoral and cellular immune responses. MBL does not recognize self-components or glycoproteins from other higher animals due to the presence of terminal sialic acid or galactose that interrupts the repeating carbohydrate structures. A number of membrane receptors for MBL, including C1q phagocytic receptor (C1qRp), calreticulin (also known as C1qR), and CR1 (CD35), have been described. Interactions with these receptors may also be important in stimulating phagocytosis.
Mouse MBL-1 and MBL-2 are produced primarily in the liver and are secreted into the blood stream. In addition, mouse MBL-1 is also expressed in lung, kidney, and testis while MBL-2 is expressed in kidney, thymus, and small intestine.

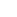
|
ng/ml |
O.D. |
Average |
Corrected |
|
|
0.00 |
0.0068 |
0.0089 |
0.0079 |
|
|
0.03 |
0.0184 |
0.0191 |
0.0188 |
0.0109 |
|
0.08 |
0.0431 |
0.0464 |
0.0448 |
0.0369 |
|
0.25 |
0.1218 |
0.1243 |
0.1231 |
0.1152 |
|
0.74 |
0.3541 |
0.3709 |
0.3625 |
0.3547 |
|
2.22 |
0.9895 |
1.0440 |
1.0168 |
1.0089 |
|
6.67 |
2.2540 |
2.3080 |
2.2810 |
2.2732 |
|
20.00 |
3.8100 |
3.8060 |
3.8080 |
3.8002 |
|
Intra-assay Precision |
Inter-assay Precision |
|||||
|
Sample Number |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
|
22 |
22 |
22 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
|
|
Average(pg/ml) |
5558.1 |
1836.6 |
373.7 |
5910.8 |
1881.4 |
382.7 |
|
Standard Deviation |
194.1 |
55.8 |
15.7 |
171.4 |
52.1 |
9.5 |
|
Coefficient of Variation(%) |
3.5 |
3.0 |
4.2 |
2.9 |
2.8 |
2.5 |
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay) Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays) Three samples of known concentration were tested six times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
The recovery ranged from 89% to 118% with an overall mean recovery of 102%.
| Sample Matrix | Sample Evaluated | Range (ng/ml) | Detectable (%) | Mean of Detectable (ng/ml) |
| Serum | 30 | 154.5-547.4 | 100 | 293.8 |
Serum/Plasma – Thirty samples from apparently healthy volunteers were evaluated for the presence of MBL2 in this assay. No medical histories were available for the donors.
 New Products
New Products